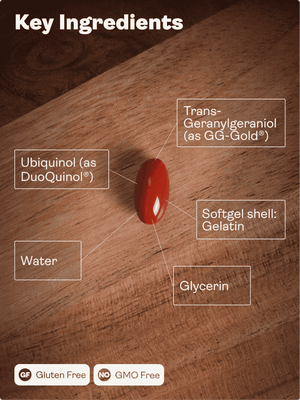
A coenzima Q10 (CoQ10) é um composto essencial para a produção de energia celular. É produzida pelo organismo mas, à medida que envelhecemos, a sua produção diminui. Descubra por que razão a CoQ10 é essencial para abrandar o processo de envelhecimento e como pode aumentar os seus níveis.
Já alguma vez parou para imaginar os milhares de processos bioquímicos que ocorrem no seu corpo a cada minuto? Para a maioria de nós, passamos pela vida alegremente inconscientes de tudo o que se passa nas células do nosso corpo.
No entanto, para se sentir mais jovem durante mais tempo, é importante compreender como funcionam alguns destes processos, de modo a poder apoiar corretamente o seu corpo à medida que este envelhece. Por exemplo, sabia que existem processos enzimáticos cruciais que são responsáveis pela geração de energia no nosso corpo e que estes têm uma influência direta na nossa saúde e no processo de envelhecimento?
Neste artigo, vamos analisar uma coenzima em particular que é popular no mundo do anti-envelhecimento e da saúde: a coenzima Q10. Iremos abordar brevemente o que faz, porque é importante e como pode tomar um suplemento de CoQ10 para manter os seus níveis de energia elevados.
O que é o Q10?
As nossas células e todos os processos do nosso corpo dependem de reacções químicas. Por exemplo, uma grande parte do processo que converte os alimentos em energia é um processo químico. As moléculas que causam e controlam estas reacções são chamadas enzimas. As enzimas são moléculas de proteínas que estão localizadas em organelos dentro da célula ou que estão a flutuar no próprio corpo celular.
As coenzimas são uma família de moléculas orgânicas não proteicas que ajudam as enzimas a catalisar e a controlar as reacções. Conseguem-no ligando-se à enzima num local específico que a ativa e ajuda a enzima a provocar a reação. Do ponto de vista bioquímico, sem os coenzimas, haveria menos ou nenhumas reacções a ocorrer no corpo.
A coenzima Q10 pertence a uma família e e de coenzimas conhecida como coenzima Q ou ubiquinona e é encontrada principalmente nas células humanas. Os restantes membros da família (6 deles) são encontrados em animais e bactérias.
A CoQ10 é armazenada nas mitocôndrias, a central de energia da célula. As maiores quantidades desta coenzima encontram-se no fígado, no coração, no cérebro, nos músculos e nos rins. É também solúvel em lípidos, o que lhe permite atravessar facilmente a membrana celular e as membranas externa e interna das mitocôndrias.
Coenzima Q10 Utilizações e benefícios
A coenzima Q10 desempenha um papel essencial ao ajudar o nosso corpo a produzir e regular a energia. A maioria das células do nosso corpo necessita de energia suficiente para funcionar corretamente, razão pela qual a CoQ10 é tão importante.
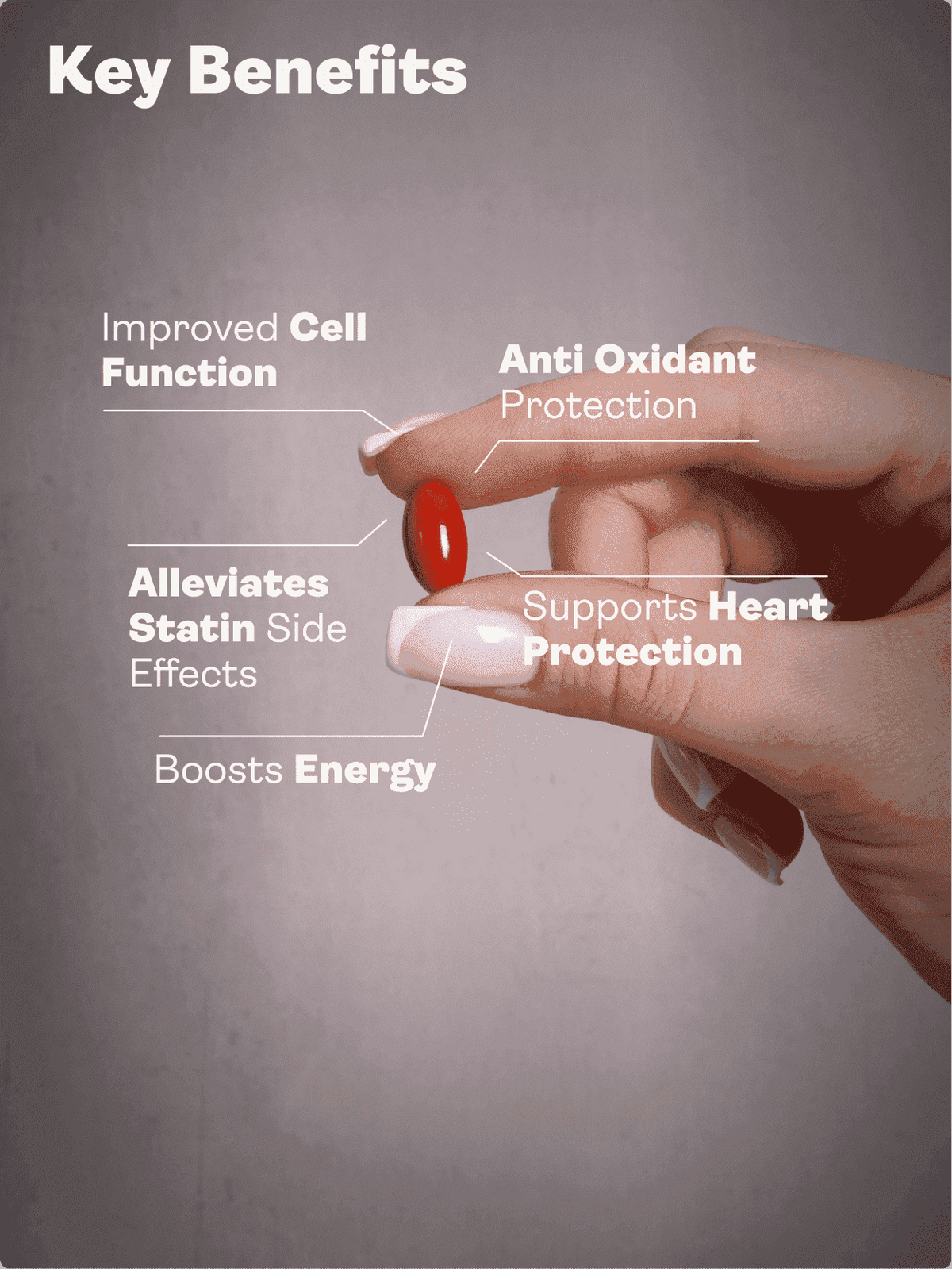
É também um antioxidante lipídico muito importante que impede o nosso organismo de gerar radicais livres em excesso e de modificar o ADN, os lípidos e as proteínas. Protege e apoia as mitocôndrias que produzem a energia de que as nossas células necessitam.
Em suma, a toma de um suplemento de coenzima Q10 não só melhora o funcionamento das mitocôndrias, como também as protege, bem como os tecidos e os órgãos do seu organismo.
CoQ10 gera energia - Como?
Para compreender o funcionamento da CoQ10, é necessário analisar brevemente a glicólise (decomposição da glicose) e os processos da cadeia de transporte de electrões.
Glicólise
A glicólise é uma via metabólica que consiste em 10 reacções que ocorrem todas no citoplasma de uma célula. O citoplasma é o líquido no interior da célula, um pouco como a clara de um ovo. As reacções quebram as moléculas de glucose dos nutrientes para produzir um composto orgânico chamado trifosfato de adenosina (ATP).
O ATP fornece a energia de que as células necessitam para alimentar processos como a síntese química, a contração dos músculos e a propagação dos impulsos nervosos.
A glicólise ocorre em duas fases:
-
Fase de investimento energético: Nesta fase, o organismo "investe" a energia de 2 moléculas de ATP para dividir uma molécula de glucose ao meio.
-
Fase de recuperação de energia: As duas metades da molécula de glucose são então oxidadas para produzir duas moléculas de piruvato (compostos químicos importantes). Neste processo, são produzidas 4 moléculas de ATP e 2 moléculas de NAD+ que são reduzidas a NADH.
As moléculas de piruvato são então transportadas para a mitocôndria por transportadores especiais de piruvato. Lá, elas sofrem oxidação para produzir acetil coenzima A, NADH, flavina adenina dinucleótido(FADH2) e dióxido de carbono.
O NADH gerado no citoplasma tem de ser transportado através da membrana interna da mitocôndria para a matriz (parte da mitocôndria que produz energia e desempenha outras funções). Infelizmente, a membrana é impermeável tanto ao NAD+ como ao NADH. Por esta razão, os electrões do NADH têm de ser transportados através da membrana para a matriz através de um processo denominado cadeia de transporte de electrões.
A cadeia de transporte de electrões (ETC)
A ETC tem quatro complexos que envolvem a transferência de electrões do NADH através da membrana interna da mitocôndria para a matriz para produzir ATP. Esta cadeia é muito importante porque produz 95% da energia da célula.
A Coenzima Q10 tem um papel vital a desempenhar para garantir que os electrões são transportados e que o ATP é formado. Sem CoQ10 suficiente, haverá menos ATP produzido nas nossas células, o que tem um efeito negativo na função celular e, eventualmente, na nossa saúde.
A coenzima Q10 é anti-envelhecimento?
Sim, a coenzima Q10 desempenha um papel muito importante na prevenção do envelhecimento precoce. Sem ela, as nossas células perderiam a capacidade de produzir energia e a proteção antioxidante que ela oferece.
Além disso, embora os nossos corpos possam sintetizar a coenzima Q10 naturalmente, num estudo de 2019, publicado no National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), foi demonstrado que, à medida que envelhecemos, os nossos níveis de CoQ10 tendem a cair. De facto, muitas condições crónicas associadas ao envelhecimento têm sido associadas a baixos níveis desta coenzima.
Ao aumentar os níveis desta enzima, pode potencialmente abrandar ou mesmo prevenir estas condições e a deterioração que está associada ao envelhecimento. Por conseguinte, a CoQ10 é, em grande medida, anti-envelhecimento.
Existem benefícios na toma de suplementos de coenzima Q10?
Sim, foram efectuados numerosos estudos sobre a CoQ10 e o seu efeito em várias doenças. Aqui estão alguns dos possíveis benefícios que foram encontrados. A investigação sobre este antioxidante essencial está em curso.
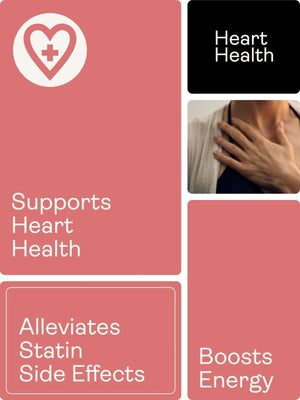
A CoQ10 pode melhorar os sintomas das pessoas que sofrem de insuficiência cardíaca
A insuficiência cardíaca ocorre quando os músculos do coração são incapazes de se contrair ou relaxar o suficiente para bombear o sangue. O tecido muscular cardíaco é constituído por células como os cardiomiócitos, as células musculares lisas e os fibroblastos. Estas células utilizam o ATP das suas mitocôndrias para alimentar a sua contração. Num estudo que envolveu doentes com insuficiência cardíaca, a administração de coenzima Q10 melhorou os seus sintomas.
Pode melhorar o desempenho no exercício físico
O stress oxidativo e as mitocôndrias disfuncionais podem limitar a sua capacidade de fazer exercício. Sem níveis suficientes de energia celular, os músculos não conseguem contrair-se para sustentar um treino. A coenzima Q10 desempenha ambos os papéis, como um antioxidante e um componente crítico na produção de energia celular. Num estudo de 2010, foi demonstrado que a toma de suplementos com coenzima Q10 ajudou a reduzir o stress oxidativo e aumentou a potência durante o exercício.
Pode ajudar a regular os níveis de açúcar no sangue
Existe uma forte ligação entre as mitocôndrias disfuncionais e a resistência à insulina. Num estudo de 2014, pacientes com diabetes tipo 2 tomaram suplementos de CoQ10 durante 12 semanas. O resultado foi uma redução dos níveis de açúcar no sangue com diminuições notáveis da hemoglobina A1c e dos níveis de açúcar no sangue em jejum.
Se tem problemas com os níveis de açúcar no sangue, leia:Berberina, o super antioxidante
A coenzima Q10 pode ajudar a minimizar os sinais de envelhecimento
Os radicais livres no tecido cutâneo, provenientes de entidades ambientais e celulares, causam stress oxidativo. Se não for controlado, este pode danificar a sua pele. A CoQ10 é um poderoso antioxidante. Os tratamentos tópicos que contêm CoQ10 são normalmente aplicados para contrariar o stress oxidativo e aumentar a produção de energia das células da pele, mantendo a sua pele com um aspeto jovem e saudável.
O nosso produto, Injuv, éum hidratante totalmente natural que melhora a sua pele e os sinais de envelhecimento a partir do interior.
A CoQ10 pode ajudar a proteger os pulmões
Como mencionado, esta coenzima é um poderoso antioxidante que desempenha um papel importante na minimização dos danos causados pela oxidação.
As doenças pulmonares crónicas, como a Doença Pulmonar Obstrutiva Crónica (DPOC), estão associadas a danos oxidativos e a níveis baixos de coenzima Q10 nos pulmões. A investigação indica que a toma de um suplemento com esta coenzima pode ajudar a aliviar alguns dos sintomas associados a estas doenças.
A coenzima Q10 pode também ajudar nas enxaquecas e nos efeitos secundários das estatinas
Outros estudos também indicam que a CoQ10 tem o potencial de reduzir e possivelmente prevenir enxaquecas. Os investigadores pensam que isto pode dever-se ao facto de manter saudáveis as mitocôndrias nas células cerebrais.
Há também indicações de que a CoQ10 pode ajudar a combater a fraqueza muscular e, possivelmente, a gerir a dor associada à utilização de estatinas.
A coenzima Q10 pode ser obtida através dos alimentos?
Sim, é possível obter a coenzima Q10 através dos alimentos, no entanto, estes apenas contribuem com 25% das necessidades do organismo e não aumentam significativamente os níveis de CoQ10 no organismo. Em média, a ingestão de CoQ10 através da dieta é de cerca de 3 a 6 mg/dia. Isto faz com que os suplementos sejam a opção ideal para aumentar as concentrações de CoQ10 nos tecidos.
Os alimentos que contêm coenzima Q10 incluem:
-
Carnes de órgãos: Como o coração, os rins e o fígado.
-
Carne muscular: Como frango, vaca e porco.
-
Peixes gordos: Como a sardinha, o arenque, a cavala e a truta.
-
Vegetais: Como os espinafres, a couve-flor e os brócolos.
-
Leguminosas: Soja, amendoins e lentilhas.
Vale a pena tomar CoQ10?
Sim, devido ao papel crítico que a CoQ10 desempenha na produção de energia e na saúde, e ao facto de os níveis diminuírem com a idade, vale a pena tomar um suplemento com esta enzima. Se acha que está a lutar contra o cansaço crónico, a fadiga, o nevoeiro cerebral e a função cerebral lenta, beneficiará da suplementação com a coenzima Q10.
No entanto, existe um problema com os suplementos tradicionais. Quando administrada por via oral, apenas 5% da CoQ10 chega ao sistema circulatório devido ao sistema digestivo. Os doentes com uma deficiência desta coenzima necessitam de doses farmacológicas muito mais elevadas e os métodos tradicionais de administração podem não ser tão eficazes.
No entanto, graças à tecnologia, novos métodos de administração, como os suplementos lipossómicos, podem fornecer nutrientes diretamente à célula, o que aumenta a biodisponibilidade e os benefícios da suplementação com CoQ10.
Para saber mais sobre a administração lipossomal, leia: O que são suplementos lipossomais e como funcionam?
Conclusão
A coenzima Q10 está no centro dos processos bioquímicos mais importantes. Desempenha um papel fundamental na cadeia de transporte de electrões, facilitando assim a produção de energia celular. Níveis extremamente baixos de coenzima Q10 podem ter efeitos desastrosos no seu corpo e têm sido associados a muitas das doenças crónicas associadas ao envelhecimento.
O stress oxidativo, que afecta a maioria dos órgãos do corpo, incluindo a pele, pode destruir as células e acelerar o envelhecimento e a morte. Os benefícios da coenzima 10 para a saúde são transversais, desde o cérebro ao sistema nervoso, aos músculos cardíacos e até aos pulmões.
Embora o corpo sintetize naturalmente a CoQ10, a idade atrasa o processo. A segunda fonte da coenzima é a alimentação. No entanto, esta também não contribui muito. Se quiser aumentar os seus níveis de CoQ10 para parecer mais jovem durante mais tempo e retardar o envelhecimento, considere a suplementação com coenzima Q10 lipossómica.
O conteúdo deste artigo tem apenas um objetivo informativo. Não se destina a substituir o aconselhamento, diagnóstico ou tratamento médico profissional. Procure sempre o conselho do seu médico ou prestador de cuidados de saúde antes de iniciar um novo regime ou programa de saúde. Não ignore o aconselhamento médico nem adie a sua procura devido a algo que tenha lido neste sítio ou em qualquer produto Youth & Earth .